MIKAIA University Application Note: Immune cell infiltration in tumor micro environment (TME)
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a histological method used to detect specific protein markers, which in turn are important in tumor diagnosis and classification. A common question is the quantitative detection of positive (e.g., DAB+) cells. For this regard we have developed the IHC Cell Detection App to count positive (DAB+) and negative (H+) cells in various IHC stainings to calculate statistics such as the amount of cells and cell density in cells/mm2.
What specific protein is marked by the chromogen (e.g., DAB) depends on the used antigen. The app is designed to be compatible with a wide range of antigens, including nuclear or cytoplasmic antigens. An example use case is to detect and quantify CD3+, CD4+ or CD8+ lymphocytes inside and outside of the metastasis or tumor.
In spite of its name, the app can also be used to detect distinctly stained cells in other non-IHC stains. This is possible by configuring a custom stain using the stain estimation dialog. The IHC Cell Detection App will internally separate both stains. If no custom stain was configured, it will assume a default H-DAB stain. For simplicity, the remainder of this app note will assume the common H-DAB stain.
App Description Table
| Input | |
| Staining | IHC duplex stains, e.g., H-DAB. By using the stain configuration / stain estimation feature, any other stains incl. non-IHC, where target cells are stained in a distinct color, can also be analyzed. |
| Microscopy mode | Brightfield |
| Magnification | Typically 20x or 40x. |
| Supported Analysis Modes | ROI, FoV, Slide, Batch |
| Outputs | |
| Graphical Outputs | Positive cells outlined in red – [optional] negative cells outlined in blue. – [optional] Tissue outlined in green. – [optional] circular hotspots – [optional] dynamic size clusters in yellow – [optional] density heatmap of positive cells |
| Slide-level output metrics | – Pos. Cells / mm²absolute number of pos. and neg. cells – % pos. cells of all cells – # hotspots – tissue area in mm² |
| Description | |
| Post-processing / additional options | – find hotspots of positive cells – group cells into clusters – separate positive cells by ROIs, e.g., inside and outside tumor |
| Technology / Algorithm | Based on computer vision, not AI. Algorithm can be tuned to work with various IHC markers. RGB image is first unmixed into the two separate stains, which are then analyzed independently (nuclear antigens) or in conjunction (cytoplasmic or membrane antigens) |
| Speed | A few seconds per field-of view. Typically < 5 minutes per whole-slide. |
| Use cases | – Preclinical studies – Quantify immune response to drugs – Immune cells intra-tumoral and in tumor micro environment… |
The app is used to detect positive and negative cells in nuclear IHC stainings. The workflow starts by picking a few regions in your single slide or WSIs in order to experiment with the app settings and find good parameters (e.g., detection of positive cells, sensitivity). Next, the parameters are saved as a preset, so that the parameters can be easily restored throughout the project. Afterwards define regions of interests manually or by using the Mask by Color App to count positive cells in defined areas (e.g., inside and outside tumor; in bands at increasing distance from tumor margin). Evaluate the performance (accuracy, time) and correct errors by deleting false annotations or adding missing annotations. After a successful validation, the analysis can be used for detection of cells in single slides as well as entire datasets to obtain metrics such as positive cells / mm2.
Video
Step by Step Usage
In this application note, we demonstrate how the IHC Cell Detection App can be employed in a common use case, detection of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes inside and outside of metastasis and in bands at increasing distance from tumor margin.
Configuration
First, if you would like to compute the cell density in cells/mm2, it is required to run the Tissue Detection App to detect foreground (tissue) areas in slides.
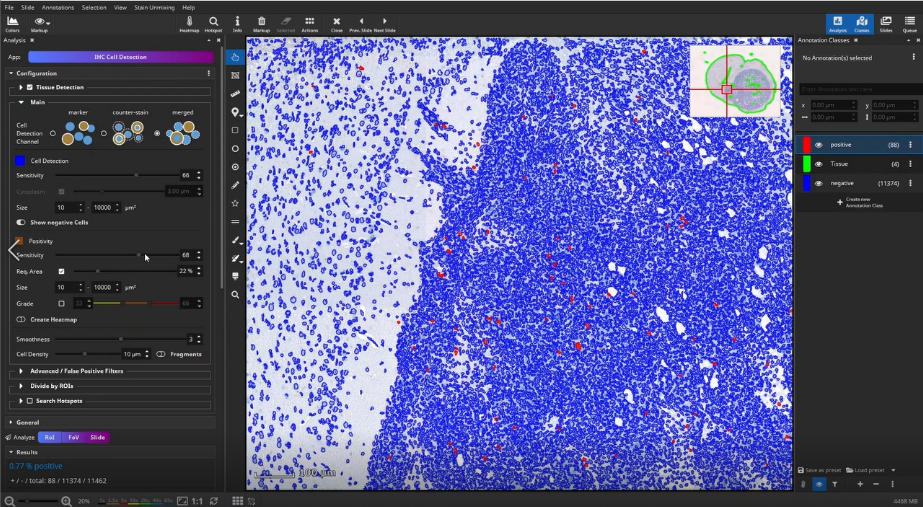
Then, positive cells can be detected in the outlined tissue, e.g., CD3+ T-cells in an IHC-stained mouse brain section. Therefore, three different cell detection channels are available. Cells can be detected directly when positive cells are solidly filled in the marker channel (e.g., DAB, marker mode). When a counter-stained nucleus is visible or sometimes visible in each positive cell, first locate cells via the Hematoxylin (counter-stain mode) or combined H-DAB channel (merged mode) and then measure the positivity separately in the nucleus or cytoplasm. Afterwards, sensitivity for positive cells is adjusted in a single field of view. For this, it is sometimes helpful to display negative cells as well, in order to increase the value to cells classified as positive. Afterwards parameters and settings are stored by creating a new preset.
Mask by Color App
To count positive cells in defined areas, e.g., inside, outside and in the tumor micro environment, you can outline ROIs manually or by using the Mask by Color App. This app enables to mask areas in slide based on their color.
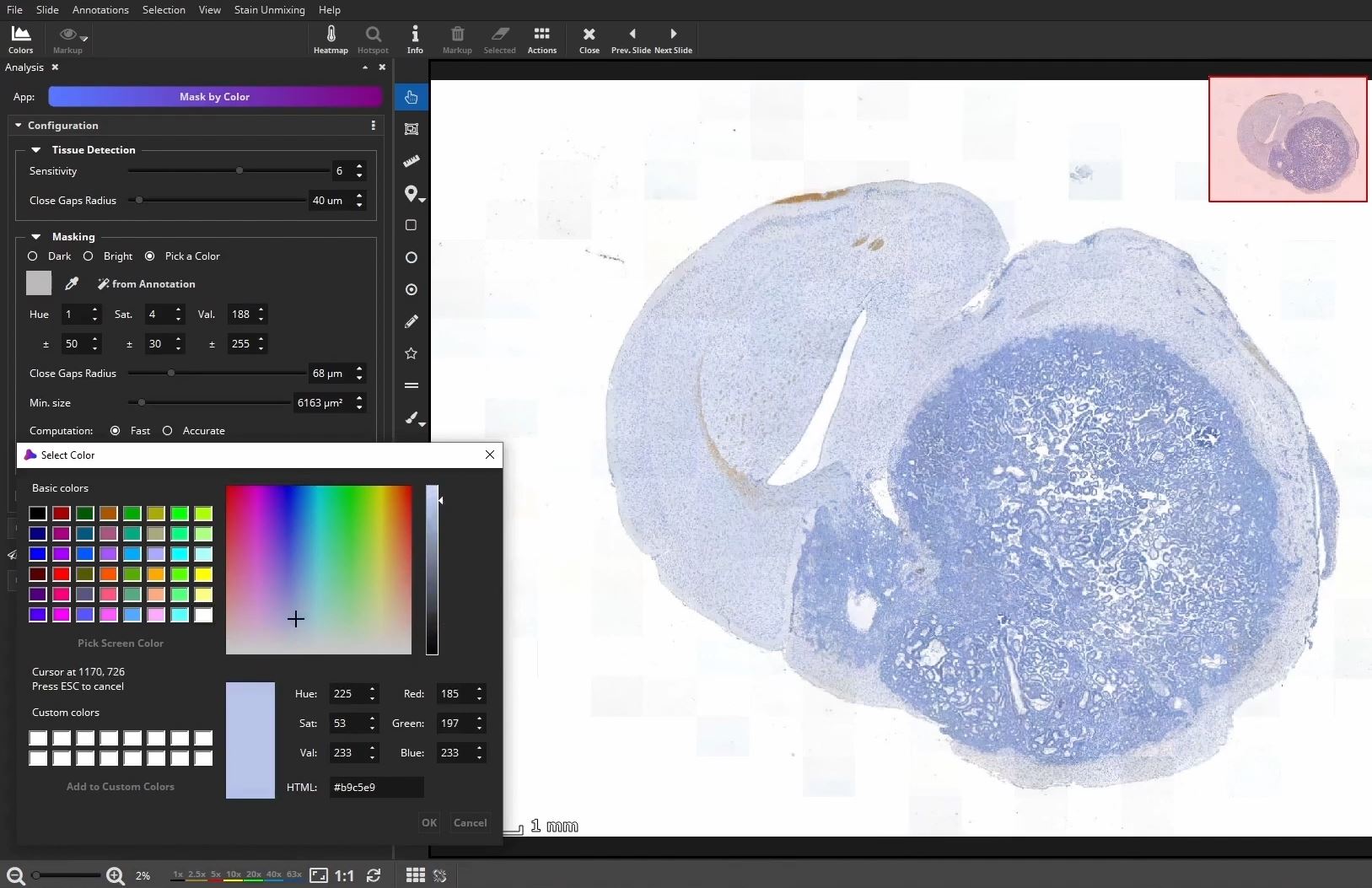
Optional: Draw or detect ROI
At first, the user marks a region of interest, e.g., a metastasis in this example, by using the color picker, which picks the color within a certain range directly in the slide.
Then, annotations outside the ROI can be removed by using the selection tool to create a clearly defined area.
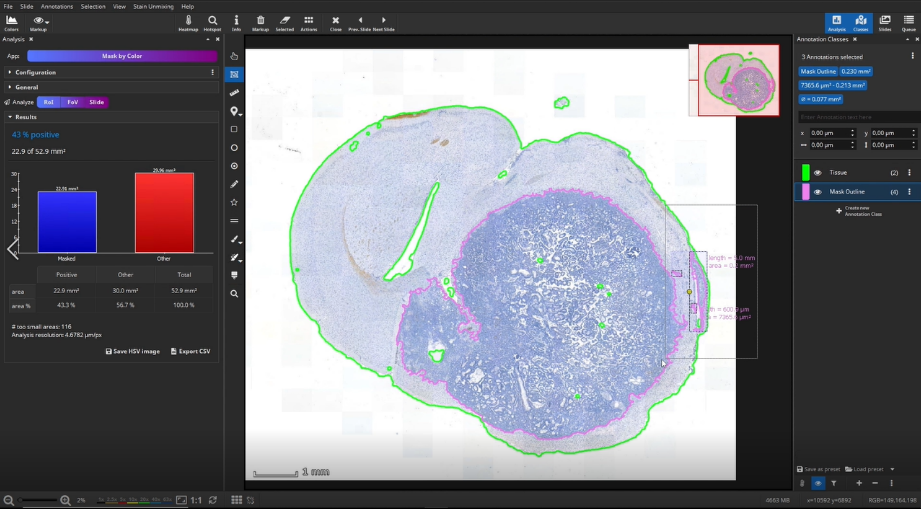
The masked area is visualized by two annotations: a mask and a polygon. We can delete the mask here and will only need the polygon, which represents the outline of the mask. We use the mask outline as the ROI, here the metastasis, for the subsequent IHC cell detection analysis.
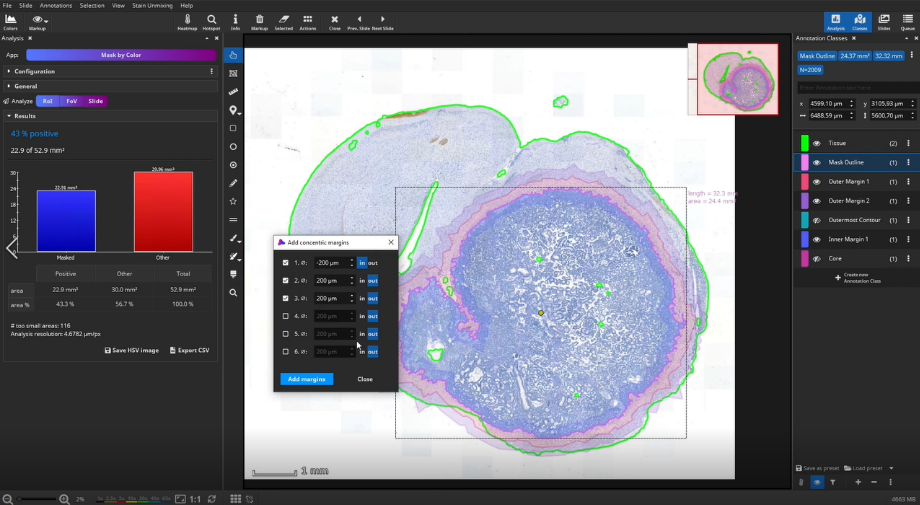
Add concentric margins
Optionally, up to three bands of custom diameters can be generated as margins around the masked area. For instance, when a tumor is masked, these bands would define the tumor environment in different distances. In addition to the 3 bands, 2 additional outline polygons around the outer band (“Outermost Contour”) and around the remaining metastasis (“Core”) are generated.
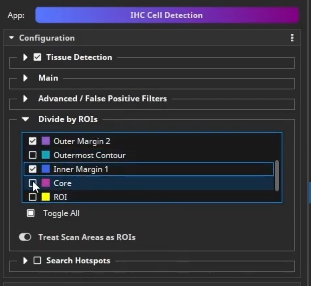
Detection of positive cells
Back in the IHC Cell Detection App, positive cells can now be detected. Load the previously created parameter preset. Next, we tell the App to group the detected cells by different ROIs. Here, it is important that only non-overlapping ROIs are selected. In this example, select Outer Margin 2, Outer Margin 1, Inner Margin 1 and Core.
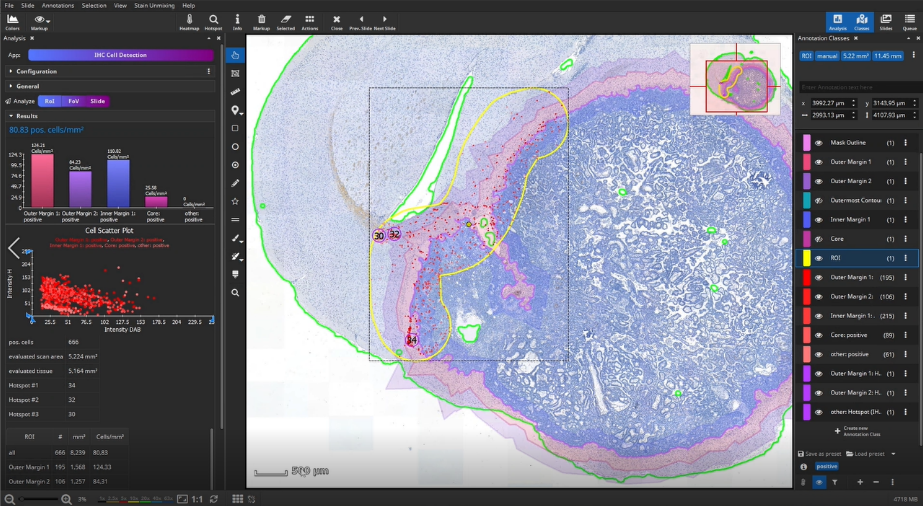
In this example, we do not analyze the entire slide, but limit the analyzed area to yet another area: in this case a segment of the metastasis interface, manually masked in yellow using the brush tool.
Select the manually created yellow ROI, and click “Analyze RoI” to detect the cells within the region outlined in yellow.
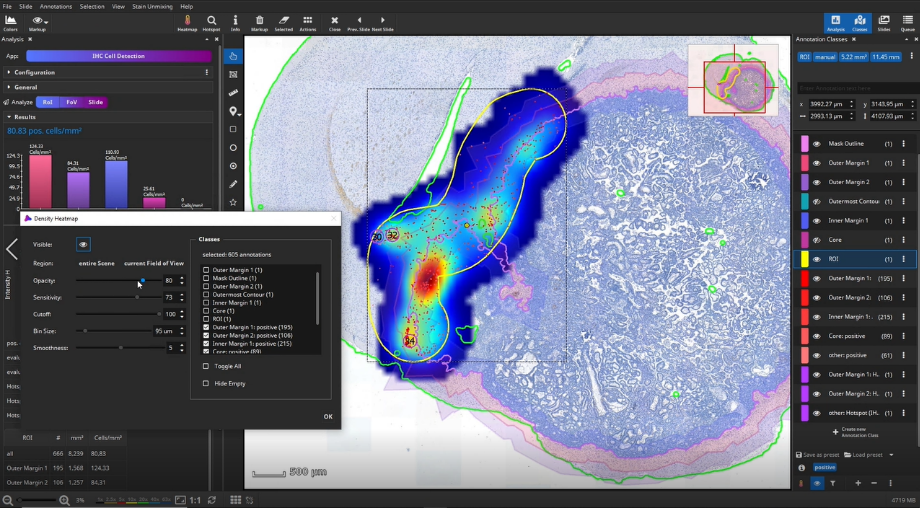
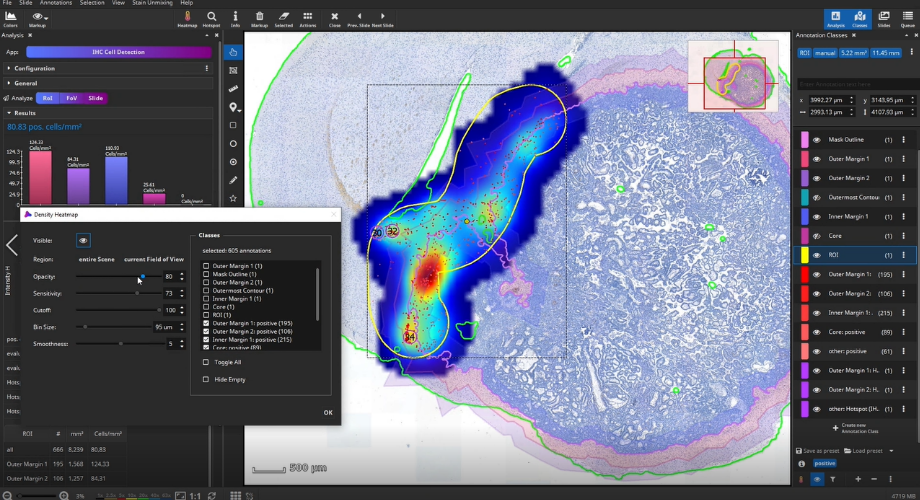
Once the analysis has finished, bar diagrams visualize cell densities per ROI in cells/mm². Furthermore, hotspots of positive cells can be displayed. The hotspot diameter as well as minimally required number of contained cells can be configured.
The detected cells can also be visualized as a density heatmap. Additionally, it would have been possible to detect cell clusters, but this post-processing step is not used in this example.
Batch analysis
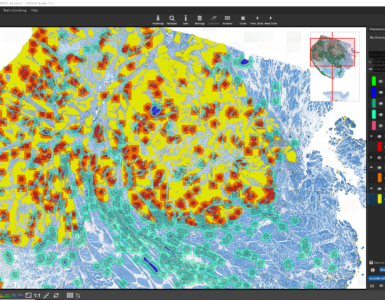
With the IHC Cell Detection App, it is possible to analyze single ROIs, an entire slide or an entire dataset comprising hundreds of slides. To start a batch analysis, import your dataset folder into the Slides panel, multi-select all slides and then the analyze “Slide” button will turn into the analyze “Batch” button. Before you “roll out” the batch analysis, it is recommended and good practice to evaluate the performance (accuracy, time) on a small test set in a quantitative or qualitative fashion first.




Add comment