Assessing risk for the Mellor Heritage Project
Manchester, UK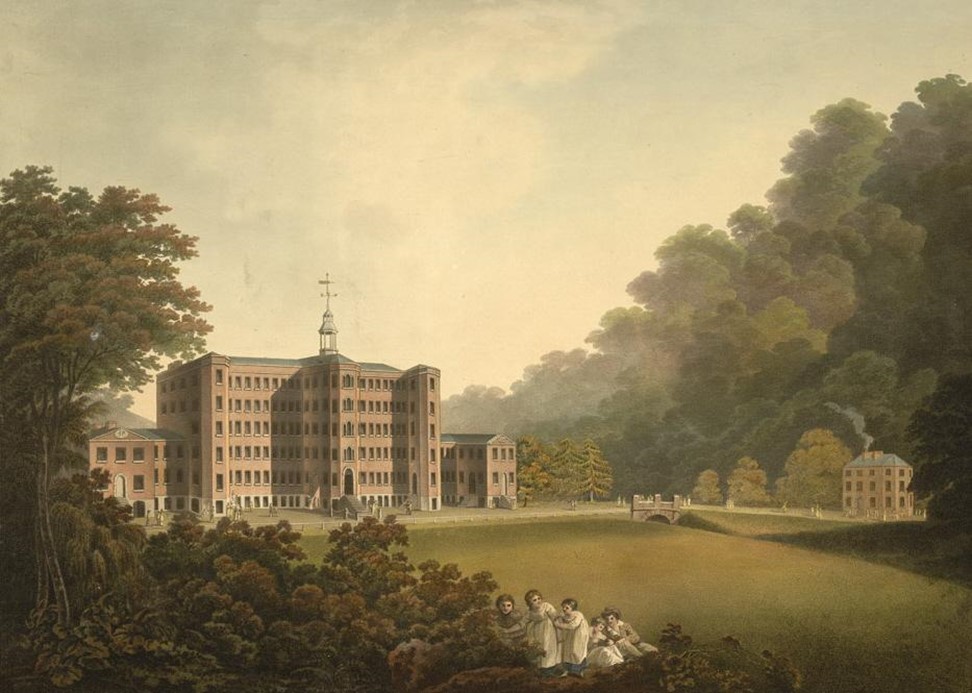
Lead
Main hazard(s)
Disaster Risk Management phase(s)
Type(s) of measure(s)
Background
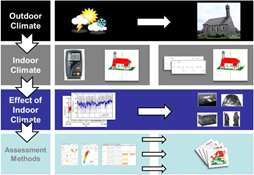
The H2020 STORM project (2016-2019), developed an integrated methodology of risk assessment and management for cultural heritage assets in response to the adverse effects of natural hazards and climate change-related events. This methodology was based on remote sensing and information technology (consisting of weather stations and a network of environmental sensors) tested in five pilot sites in Italy, Greece, UK, Portugal and Turkey. Sensors were used to monitor environmental parameters as well as deterioration processes in the cultural assets. The data was processed and analysed, generating risk maps made available at the STORM Collaborative Decision-Making Dashboard.
Each pilot site was analysed and matched with the most suitable technology according to local hazards and site characteristics. The outputs would serve to define appropriate risk treatment strategies (including risk mitigation, risk preparedness and recovery).
One of the pilot sites was the Mellor Heritage Project, in Manchester (UK). This complex includes three main sites with different micro-climatic conditions: a bronze-era burial site known as Shaw Cain located at the top of a hill and particularly exposed to extreme cold, precipitation and wind; Mellor Mill, a mill from an industrial period located by the river and particularly sensitive to humidity and freeze/thaw events; and the Old Vicarage Site, an iron-ditch sheltered by trees at one side of the hill. Sensors were placed in 30-40 locations throughout the complex, accompanied by weather stations. The data has proven to be effective in warning site managers and visiting archaeologists about weather events,as well asenabling monitoring of cracks, structural performance, electrical resistivity and sensitivity to freeze/thaw events.
Sources
For more information on Mellor Heritage Project, visit: https://www.mellorheritage.org.uk/
The Archaeological site Mellor, in Greater Manchester, was one of the project’s case studies. STORM proposes predictive models and improved methods of survey and diagnosis that will assess preventive actions and emergency responses in cultural heritage sites.
For more information on EU H2020 STORM , visit: http://www.storm-project.eu/en/project/
Other relevant sources
Neto, F. M., & Patrikakis, C. Z. (2019). Cultural Heritage Resilience Against Climate Change and Natural Hazards. Pisa University Press.